![[논문 리뷰] Dual Goal Representations](/assets/img/251120/image.png)
[논문 리뷰] Dual Goal Representations
작성자: 민예린
논문 정보
제목: Dual Goal Representations
저자: Seohong Park, Deepinder Mann, Sergey Levine, UC Berkeley.
학회: ICLR 2026
1. Introduction
- 본 논문에서는 goal-conditioned RL(GCRL)에서의 representation 방법에 대해 제안
- 목표 :
임의의 start state→임의의 target state로 최단 시간 내 도달할 수 있는 multi-task policy 학습 - navigation, object manipulation, game 등 goal-reaching framework에 적용 가능한 많은 tasks가 있음
- 목표 :
- 중요한 것은 goal을 어떻게 표현할 것인가 임
- 많은 연구들에서는 state observation을 그대로 goal state로 사용함 (ex. 길 찾기에서 도달해야 하는 최종 위치를 goal 로 사용하는 등)
- 하지만 이런 구조가 goal을 달성하기 위한 최적이 아닐 수 있고 불필요한 노이즈가 포함되기도 함
- goal을 잘 설계한다면 out of distribution goals 에 대한 robust generalization도 가능할 수 있음!
- 이상적인 goal representation이 가져야 할 두 가지 필요 조건을 소개함
- sufficiency : 충분한 정보를 포함하고 있는가
- noise invariant : goal-reaching 에 영향을 미치지 않는 불필요한 noise 를 제거했는가
contributions
dual goal representation의 이론적인 formulation과 실질적 검증
- dual goal representation이 충분히 goal 을 잘 표현하면서 noise invariant 함을 보임
- empirical recipe 가 실제로 일반화 성능을 향상 시킴을 보임
2. Preliminaries
Controlled Markov processes and goal-conditioned RL
- Controlled Markov Process (CMP) $M = (S, A, p)$
- 편의상 S, A 는 discrete spaces라고 가정 (적절한 수정을 하면 continuous space 확장 가능)
- 별도로 언급하지 않는 한 $r(s,g)=I(s=g), \ I \ is \ 0-1 \ indicator$ 로 정의함
- temporal distance function $d^\ast(s,g) =log_\gamma V^\ast(s,g)$
- deterministic 환경에서는 s에서 g 까지의 최단 경로 길이에 해당함
Exogenous Block Controlled Markov Process (Ex-BCMP)
- 본 논문에서의 일부 이론적 결과는 Ex-BCMP framework를 기반으로 함
- $Ex-BCMP = (S,Z,A,p,p_e,p_l)$
- S : observation space
- Z : latent state space
- A : Action space
- $p(z’\mid z,a)$ : latent transition dynamics
- $p_e(s\mid z)$ : observation emission distribution
- $p_l(s)$ : S → Z latent mapping function
- $s∼p_e(s∣z)$이면 항상 $p_ℓ(s)=z$가 성립한다고 가정
- Ex-BCMP는 CMP 에 noisy observation이 덧붙은 형태로 볼 수 있음
- $r_l(s,g)=I(p_l(s)=p_l(g))$로 정의함
3. Dual Goal Representation
핵심 목표 : 효과적인 goal representation $\phi(g) : S \to W$ 을 찾는 것
- W : latent representation space
3.1 The Idea
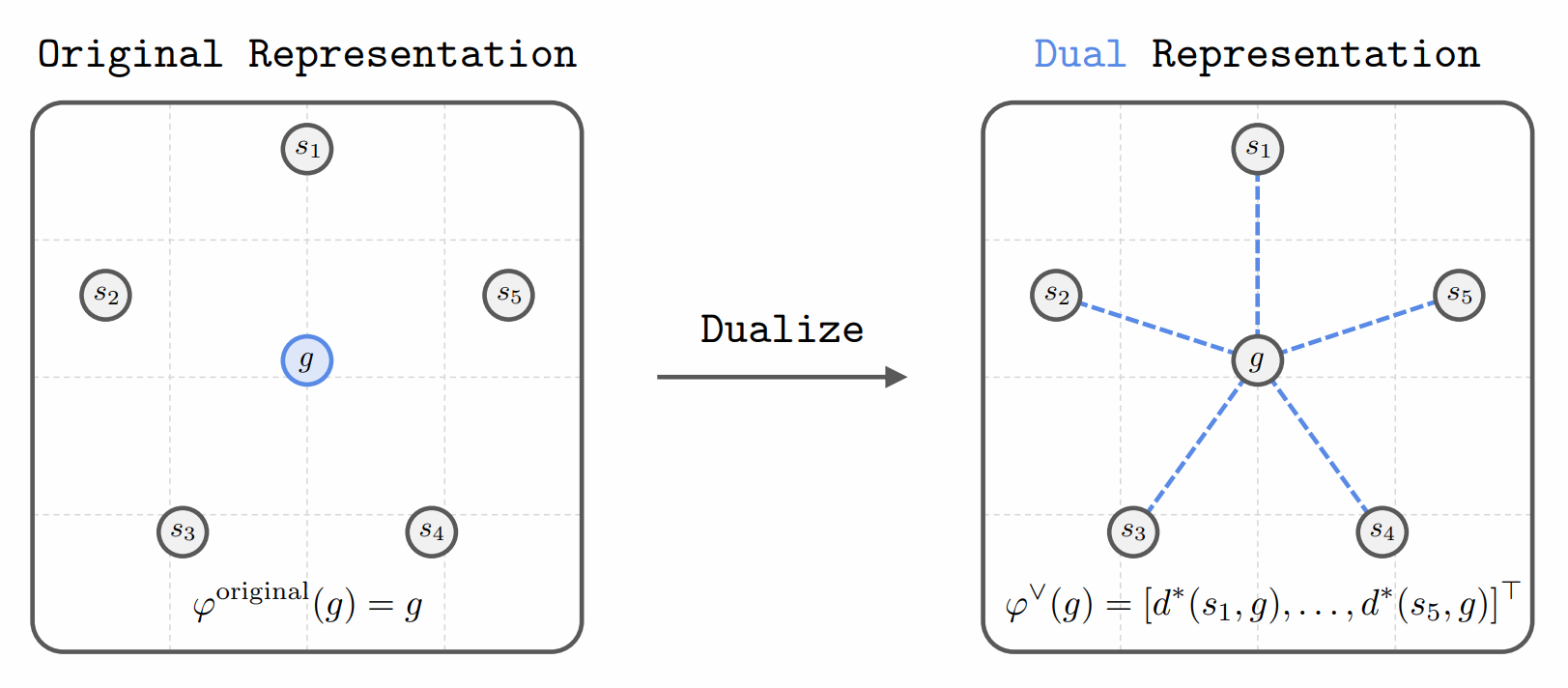
- 핵심 아이디어는 goal을 다른 모든 states로부터의 temporal distance 로 표현하는 것임
- State space $S={ s_1,s_2,…,s_K }$
- goal $\phi(g)=[d^(s_1,g),d^(s_2,g),…,d^*(s_K,g)]^\top$
- 일반적인 경우에는 $\phi$를 $S \to \mathbb{R}$인 함수로 표현하고 CMP $M=(S,A,p)$로부터 아래처럼 정의
- $\phi^∨:S \to \mathbb{R}$
→ $\phi^∨(g)=(S \to d^*(s,g))$
→ $\phi^∨(g)(s)=d^*(s,g)$
- 위 정의로 얻는 두 가지 장점이 있음
- 위 표현은 original state representation와 무관하며, intrinsic temporal dynamics에만 의존함
- 최적 goal-reaching 정책을 표현하기 위한 충분한 정보를 유지하면서 exogenous noise를 제거
3.2 Theoretical properties
정리 1. dual goal representation을 이용하면 최적 정책을 도출할 수 있음 (충분히 정보를 포함함)
증명
목적 : goal g의 raw representation이 아니라, 그 goal이 환경 전체와 맺는 temporal distance 구조.
- 즉, g라는 목표가 있을 때, 각 state에서 goal까지 얼마나 걸리는지(d)*를 $φ^∨(g)$에 담는 것
배경 :
- goal-reaching reward는 goal을 만나기 전까지 reward = 0, goal에서 한 번만 reward = 1 을 받는 구조이기 때문에 reward는 ‘goal까지 몇 step인가(d)’에만 의해 결정됨
-
reward 는 goal 도달 여부에 따른 0/1 구조이기 때문에,
$V = 0+0+0+…+0+γ^{d^∗(s,g)}⋅1$
-
- goal까지 최적 거리 $d^*(s,g)$라고 하면 optimal value는 단순히 $V^∗(s,g)=γ^{d^∗(s,g)}$ 로 표현할 수 있음
- $ϕ^∨(g)(s)=d^∗(s,g)$
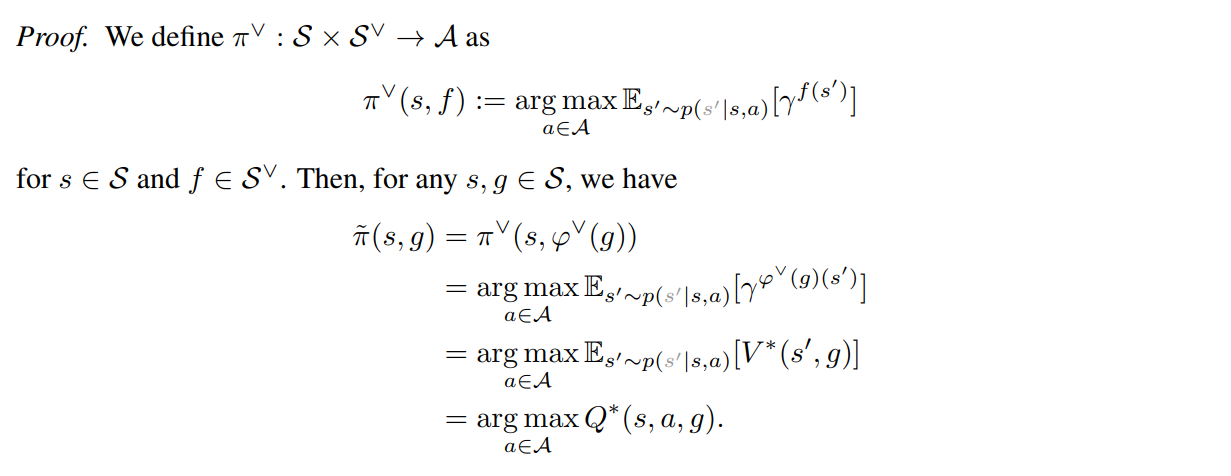
정리 2. g1/g2가 동일한 latent space를 가진다면, 동일한 dual goal representation을 가짐 (noise invariant → 서로 다른 observation이 동일한 latent space 에 맵핑됨)
증명

4. Practical Instantiation (구현)
dual goal representation을 실제로 구현하려면 두 가지 어려움이 있음
- dual goal representation은 함수형 형태이기 때문에, state space가 작고 discrete 하지 않으면 직접 구현이 어려움 (finite-dimensional vector 로 표현할 수 없음)
- temporal distance function $d^*$를 알아야 한다는 문제가 있음
Approximating functionals
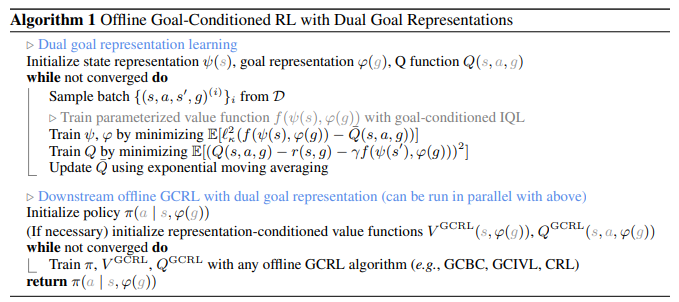
- parameterized temporal distance function 활용
- temporal distance function을 $d^∗(s,g)=f(ψ(s),ϕ(g))$ 로 모델링함
- $ψ(s)$ : state encoder (head)
- $ϕ(g)$ : goal encoder (head)
- $f(ψ(s),ϕ(g))=ψ(s)^⊤ϕ(g)$
Approximating temporal distance
- 기존 Offline RL 알고리즘인 goal-conditioned IQL 을 활용하여 $d^(s,g)$를 근사 ( $V^(s,g)$ 를 활용)
Downstream offline goal-conditioned RL
- goal-conditioned IQL을 통해 주어진 데이터셋에서 state, goal representation $ψ(s), ϕ(g)$을 학습
- representation embedding 을 활용하여 downstream policy 를 학습하며, 이때 본 논문에서는 세 가지 알고리즘을 사용
- Goal-Conditioned IVL (GCIVL)
- Contrastive RL (CRL)
- Goal-Conditioned Flow BC (GCFBC)
5. Related Work
Offline goal-conditioned RL
- offline RL 과 goal-conditioned RL의 교차점에 있는 offline goal-conditioned RL은 unlabeled (ex. reward-free) dataset으로부터 goal-reaching policy 를 학습하는 것을 목표로 함
- policies, representations, value function을 사전 학습할 수 있는 방법들을 제공하고, downstream tasks에 확장할 수 있음
- 기존 연구들은 아래 같은 접근 방법을 제안해왔음
- implicit value learning
- contrastive learning
- metric learning
- planning
- 본 연구에서는 goal representation을 효과적으로 학습하여 agent 성능을 높이는 것을 목표로 함
Representation learning for GCRL
- 선행 연구들은 $∥ϕ(s)−ϕ(g)∥_2$ 형태의 metric parameterization을 통해 temporal distance representation $\phi$를 학습, 이는 dual goal representation의 변형으로도 볼 수 있음
- 이전의 goal-conditioned RL 기반의 representation learning 에서도 유사한 접근 방법을 사용함
- 그러나 기존 연구들에서는 $\phi$을 아래 목적에 사용한다는 점이 차이가 있음
- metric-based skill learning (Park et al., 2024a)
- state representations (Ma et al., 2023)
- reward shaping (Sermanet et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2023)
- planning (Sermanet et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2023; Park et al., 2024a).
- 부가 설명
- 본 연구는 goal 자체의 representation에 집중함
- 그렇기 때문에 goal 을 충분하게 표현하고, 불필요한 noise 를 제거할 수 있음
- 그리고 metric parameterization이 아닌, 더 일반적인 inner product parameterization 을 사용한다는 점의 차이가 존재함
- 이런 차이가 더 나은 성능을 보인다는 것을 실험적으로 확인
- 부가 설명
- 기존처럼 $∥ϕ(s)−ϕ(g)∥_2$ 으로 metric representation을 하는 경우는 표현력이 부족
- 유클리디안 디스턴스 계산이 되는 구조만 가능하고, symmetric 한 성질을 가져야만 함( $∥ϕ(A)−ϕ(G)∥=∥ϕ(G)−ϕ(A)∥$ )
- 그러나 inner product 를 통해 계산된 $d$ 의 경우 symmetric 할 필요가 없음
- 기존처럼 $∥ϕ(s)−ϕ(g)∥_2$ 으로 metric representation을 하는 경우는 표현력이 부족
6. Experiments
Results with “IDEAL” Dual Representation
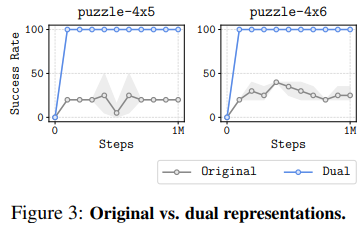
- 단순하게 discrete puzzle 환경을 사용하여 얼마나 goal 에 빨리 도달하는지 확인
- original representation vs dual representation으로 비교
- 두 방법 모두 goal-conditioned DQN으로 학습
Results on OGBench
OG bench
- 13개의 state 기반 tasks와 7개의 pixel 기반 tasks
- navigation 및 manipulation
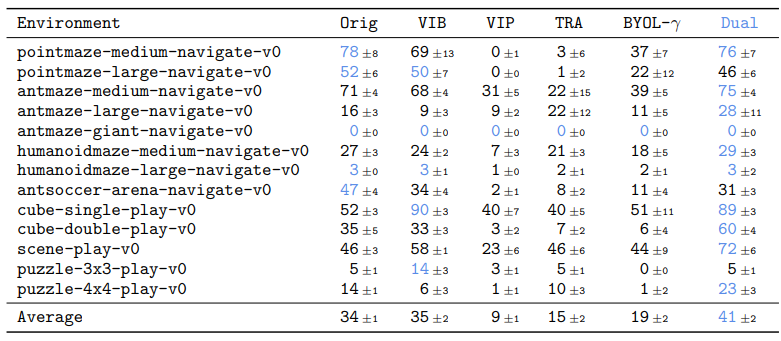
비교 알고리즘
- Original : 별도의 representation을 사용하지 않음
- VIB : variational information bottleneck을 통해 goal representation을 학습
- VIP : metric 기반 goal representation을 value learning으로 학습
- TRA : contrastive learning 기반으로 goal representation을 학습
- BYOL-γ : temporal self-supervised 방식으로 goal representation을 학습
결과
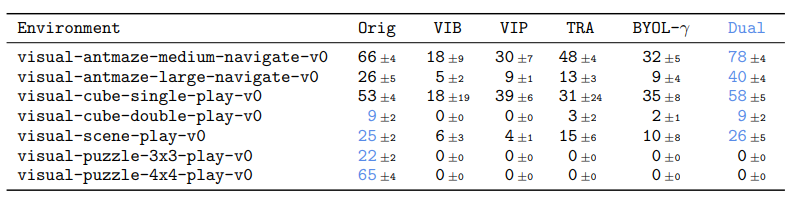
Pixel based tasks
- dual 이 5개 tasks에서는 좋은 성능을 보임
- 하지만 puzzle tasks의 경우 original 제외 모두 0 이상의 성능을 내지 못 함
- 논문에서는 early fusion / late fusion 차이 때문이라고 가정함
- original 은 s 와 g를 concatenate 하는 early fusion 사용하고, representation 은 late fusion 만 가능
- puzzle처럼 위치 정보를 활용하는 task의 경우 late fusion 에서 성능이 떨어질 수 있음
- 논문에서는 early fusion / late fusion 차이 때문이라고 가정함
7. Closing Remarks
an object is uniquely determined by its relations with every other object

